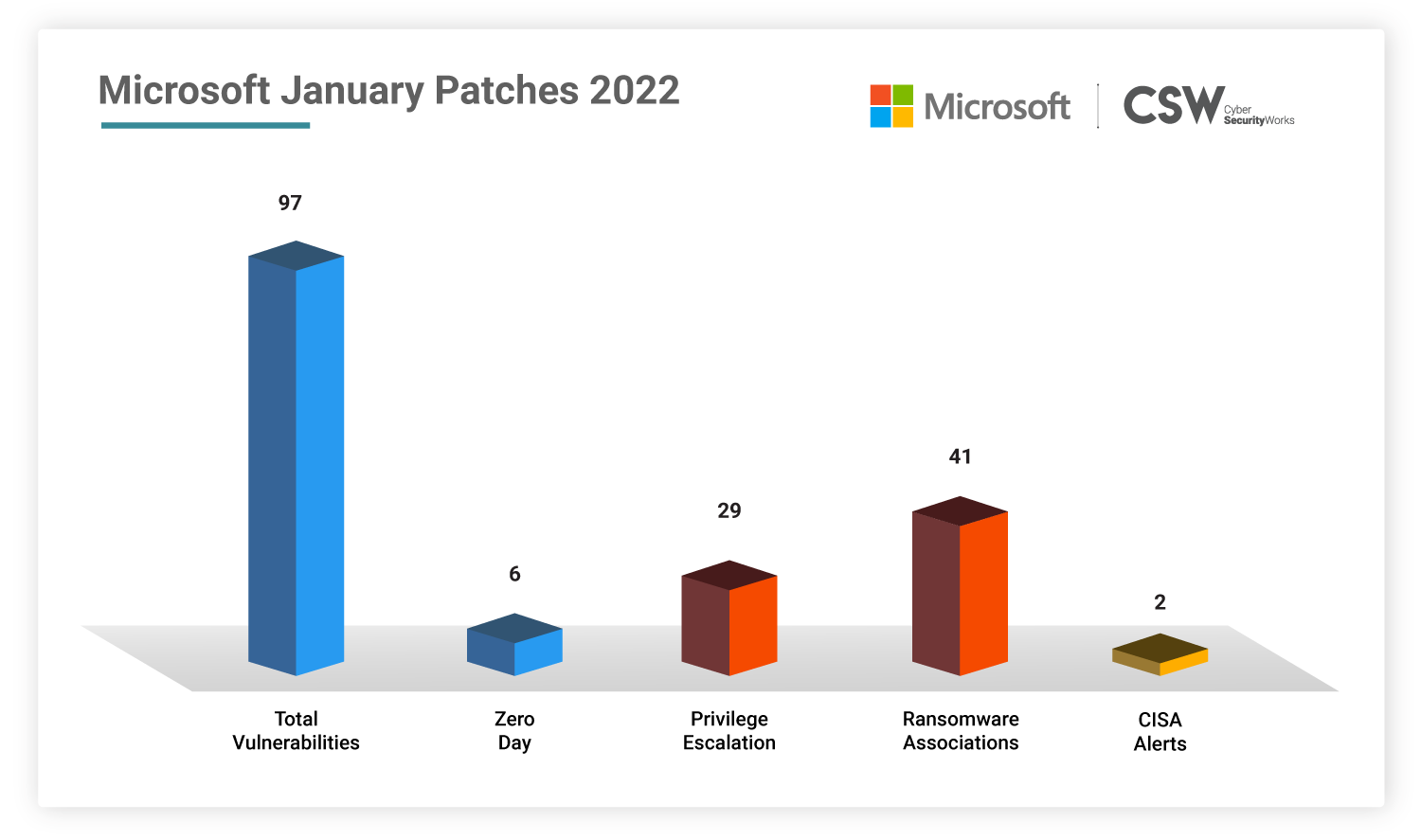
Microsoft patched 97 unique security vulnerabilities in January 2022, including six zero-days and nine critical-rated CVEs. We analyzed these weaknesses and spotlighted the most important vulnerabilities that ought to be fixed on priority.
Microsoft Patches—Overview
This January, Microsoft patched 97 vulnerabilities discovered in 2022.
-
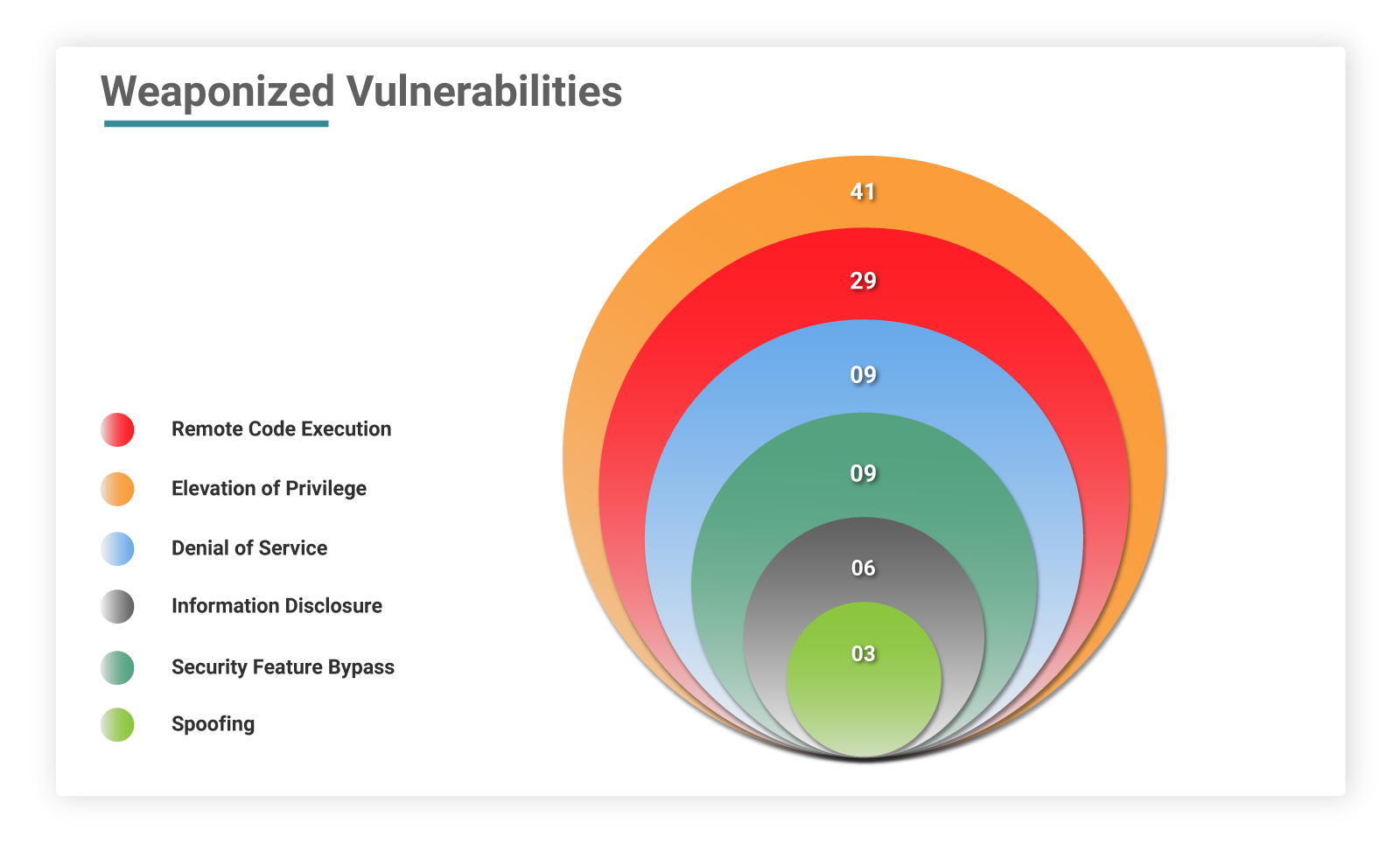
The number of CVEs classified as remote code execution bugs: 29
-
The number of CVEs with privilege escalation capabilities: 41
-
The number of CVEs linked to information disclosure: 6
-
The number of CVEs with denial-of-service capabilities: 9
-
The number of CVEs with spoofing possibilities: 3
-
The number of CVEs with security bypass: 3
Six of these issues were publicly known at the time of release, although none are currently being exploited.
Zero-Days
Microsoft had released fixes for six zero-day vulnerabilities this month in which three bugs were classified as remote code executions.
CVE-2021-22947 – Open Source Curl
CVE-2021-36976 – Libarchive
CVE-2022-21919 – Windows User Profile Service
CVE-2022-21836 – Windows Certificate
CVE-2022-21839 – Windows Event Tracing Discretionary Access Control List
CVE-2022-21874 – Windows Security Center API
None of the zero-day flaws above are known to have been exploited in the wild.
CVE-2022-21907: Wormable HTTP Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21907 uncovered in Exchange server (CVSS score: 9.8), a remote code execution flaw in the HTTP Protocol Stack. To successfully exploit this vulnerability, threat actors must transmit deliberately generated packets to targeted Windows servers, which process packets using the vulnerable HTTP Protocol Stack.
This severe wormable weakness has been discovered to affect the most recent desktop and server Windows systems, including Windows 11 and Windows Server 2022. Fortunately, the vulnerability is not actively being exploited, and no publicly announced proof of concept attacks exist.
Microsoft advises users to prioritize addressing this issue on all affected systems since it allows unauthenticated attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code in low complexity attacks.
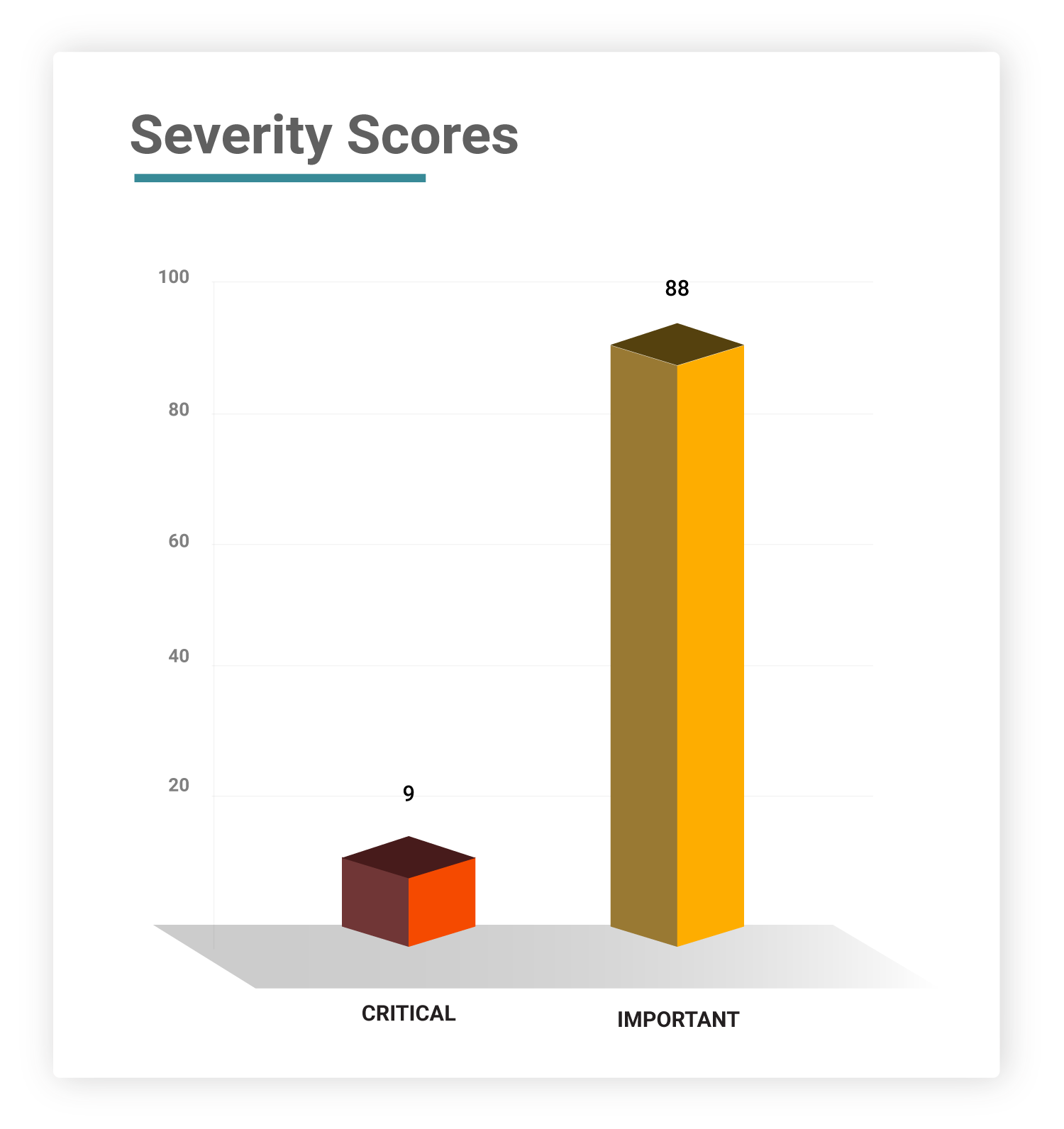
Severity
Of these 97 CVEs, nine of them are rated as critical, while six of them are zero-days.
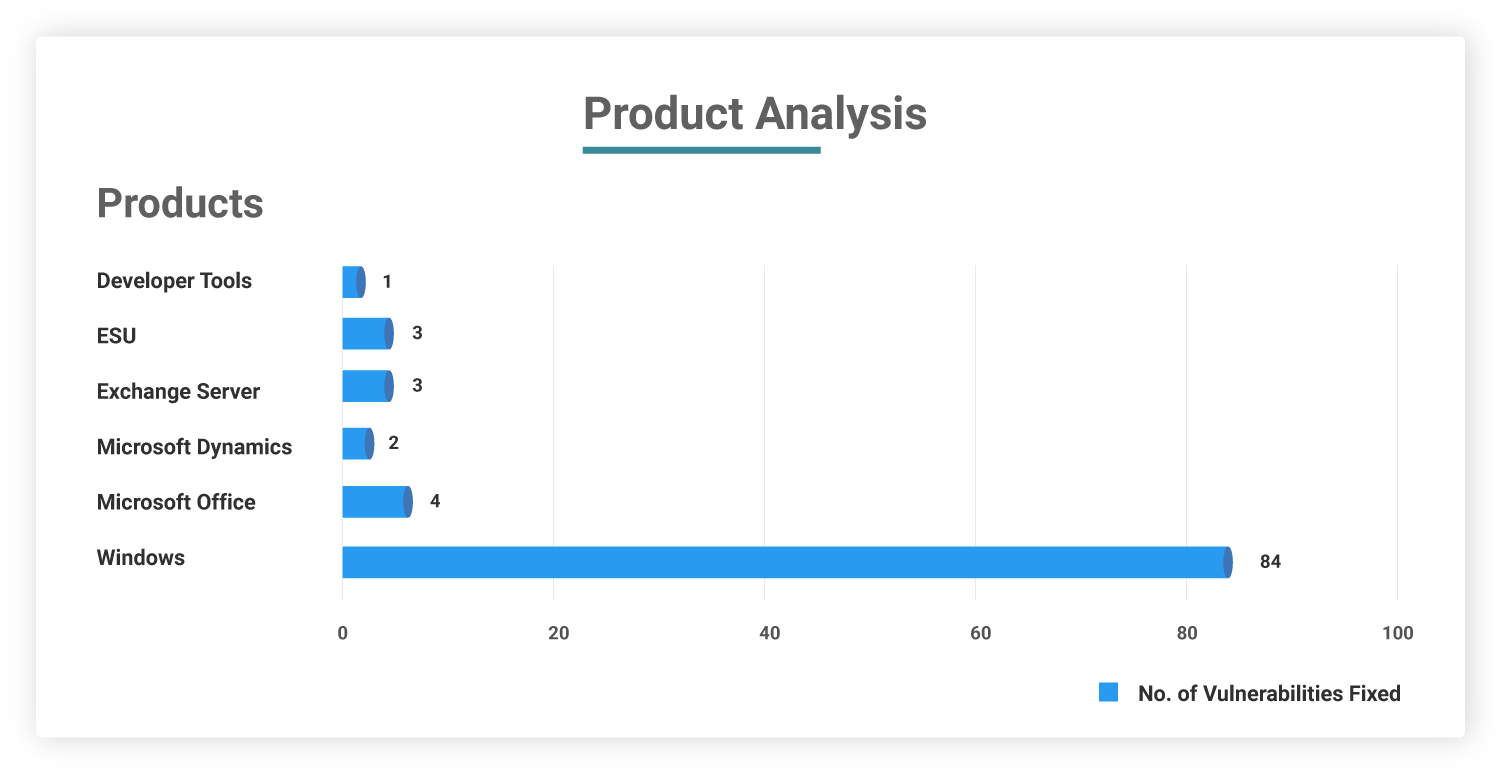
Affected Products
Affected systems include: Windows and associated components, Edge, Exchange Server, Office and related components, SharePoint Server, .NET Framework, Microsoft Dynamics, Windows Hyper-V, Windows Defender, and Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
Common Weakness Enumeration
When analyzing the weaknesses in code of these patched vulnerabilities, 41% of the CVEs are classified under the CWE-269 which leads to Improper Privilege Management. CWE-94 (Improper Control of Generation of Code) holds second place with 9%. Most concerning is that these two software weaknesses are listed under 2021 CWE Top 25 Most Dangerous Weaknesses.
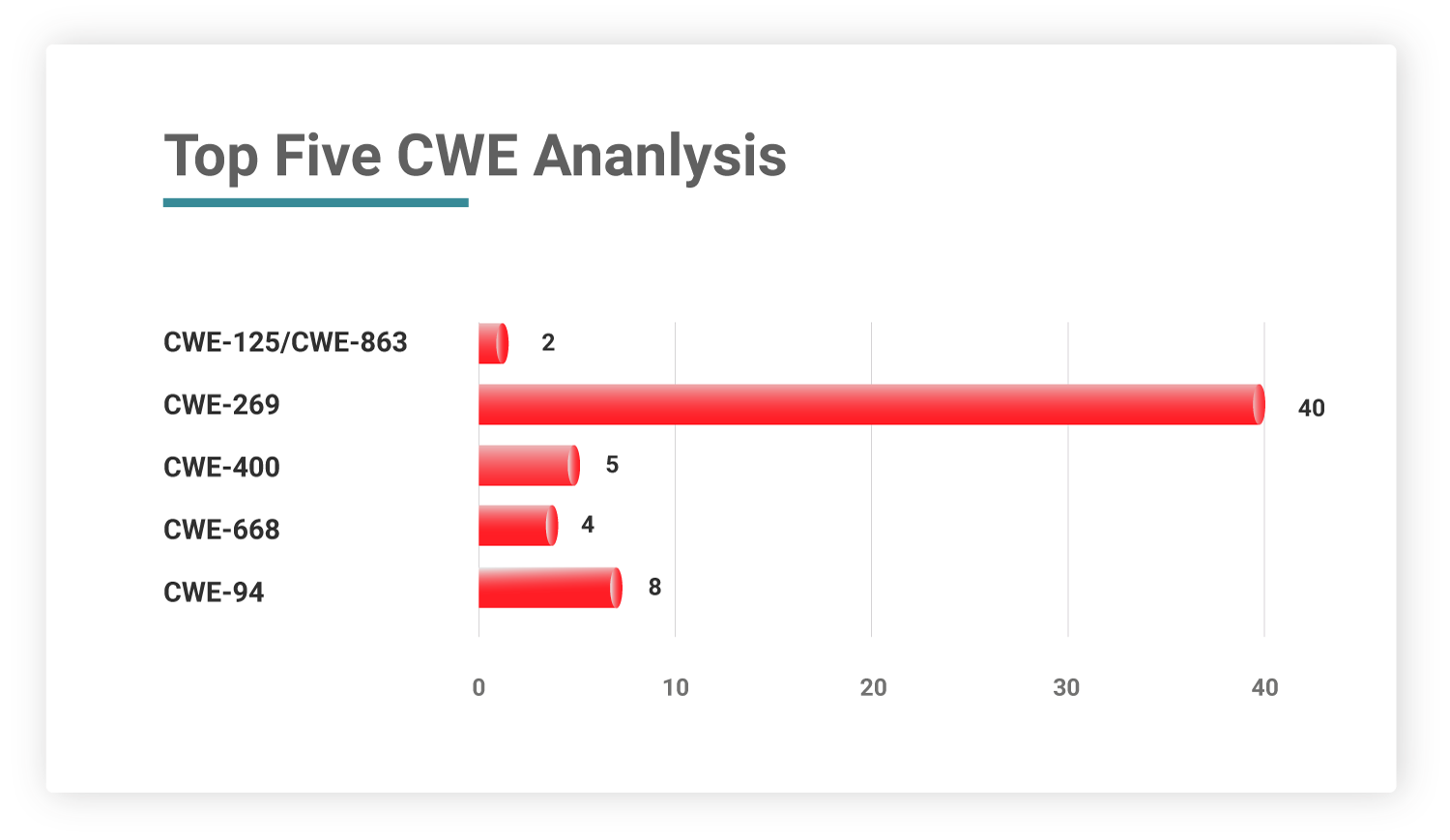
Table: Microsoft January 2022 Security Patches
On January 15, 2022, Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) has discovered evidence of a devastating malware (Master Boot Record (MBR) Wiper) campaign in Ukraine that targeted many companies. According to the researchers, powering down the victim device activates the malware, which overwrites the MBR with a ransom note; however, the ransom note is a hoax because the virus destroys the MBR and the targeted data.
In addition, CISA issued an alert suggesting that network defenders review the Microsoft advisory for strategies, techniques, and procedures relating to this activity, as well as signs of compromise. We urge Microsoft users to patch these vulnerabilities on priority.
