The recent past has seen a sudden uptick of Cl0p ransomware related activity that affects various sectors including transportation and logistics, education, manufacturing, retail, energy, aerospace, telecommunications, professional and legal services, healthcare and large tech conglomerates spanning the US, Latin America, Canada, Europe, and Asia Pacific. Considering this surge in activity, Securin experts took a deep dive into the inner workings of Cl0p ransomware.
In This Article:
Snapshot of Cl0p Ransomware’s Past
The Cl0p ransomware gang is a variant of a previously existing ransomware strain called CryptoMix, first spotted in 2019, and has been previously linked to financially motivated advanced threat groups, TA505 (GRACEFUL SPIDER) and FIN11.
In recent times, Cl0p ransomware has leveraged the Accellion File Transfer Appliance (FTA) zero-day in attacks, alongside the Solarwinds Serv-U FTP vulnerability, the GoAnywhere MFT zero-day vulnerability, the recently discovered PaperCut vulnerabilities as well as the newly discovered Progress MOVEit Transfer vulnerabilities.
The new spike in attacks has brought Cl0p back into the limelight.
Cl0p Ransomware Cheat Sheet
Securin experts have observed Cl0p ransomware exploiting a total of 13 vulnerabilities, including three recently-discovered MOVEit Transfer bugs, and two flaws affecting PaperCut print management solutions.
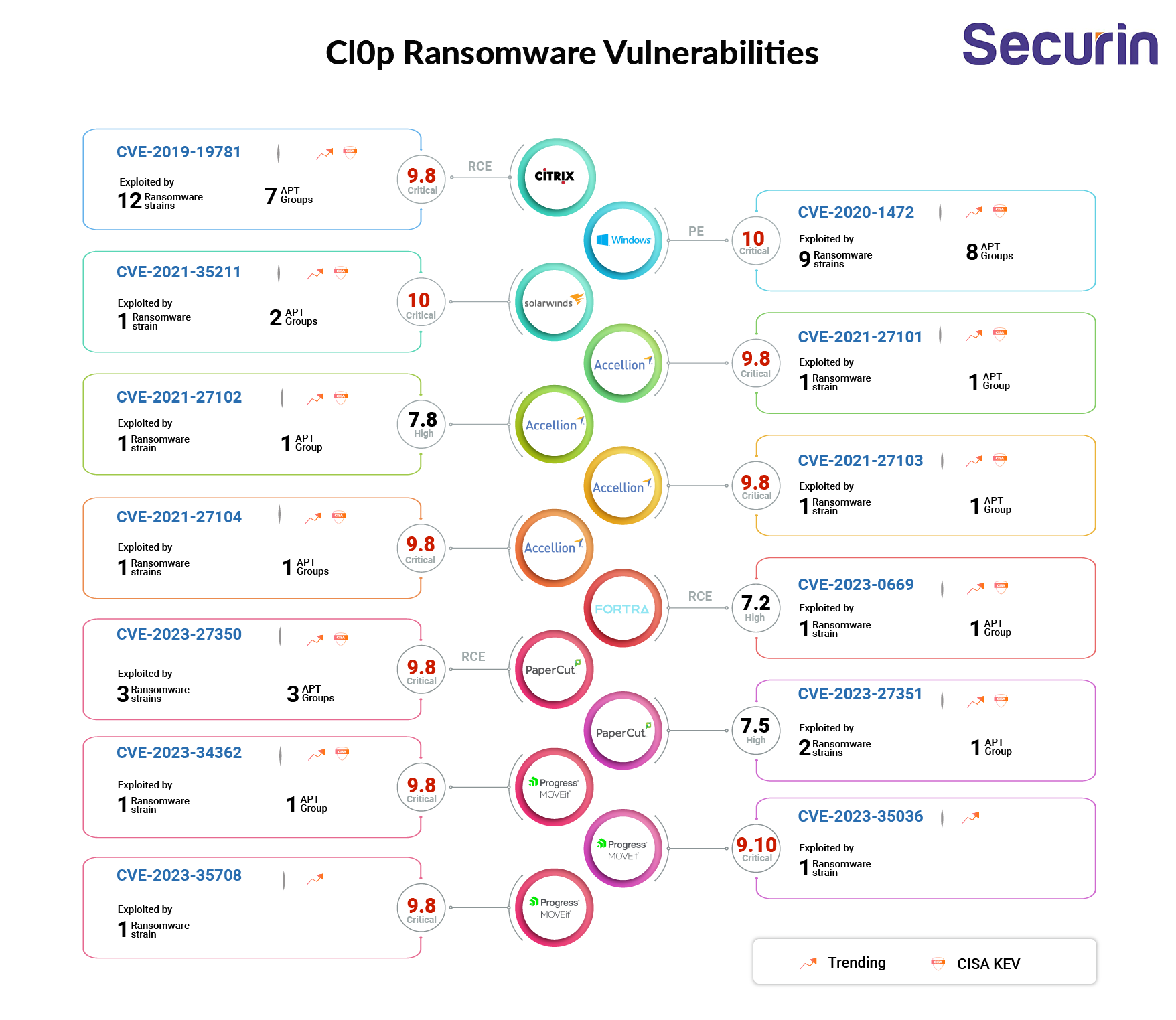
Our experts used Securin’s Vulnerability Intelligence platform for predictive analysis to identify the vulnerabilities and how likely they are to be exploited in future attacks. Here is a detailed analysis of the vulnerabilities exploited by Cl0p ransomware in their attacks:
CVE-2019-19781 - Citrix Application Delivery Controller (ADC) and Gateway 10.5 to 13.0 - CISA KEV, Trending - 12 Ransomware / 7 APT
CVE-2020-1472 - Netlogon Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability - CISA KEV, Trending - 9 Ransomware / 8 APT

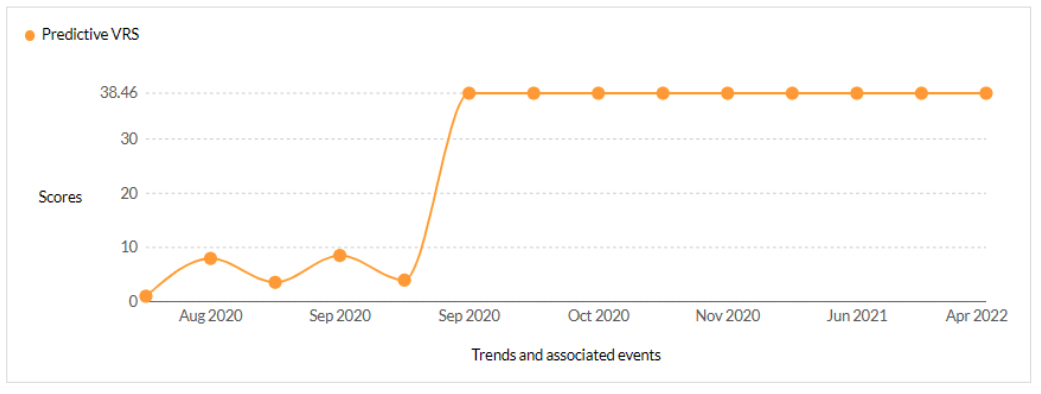
CVE-2021-35211- SolarWinds Serv-U product Remote Memory Escape Vulnerability - CISA KEV, Trending - 1 Ransomware / 2 APT
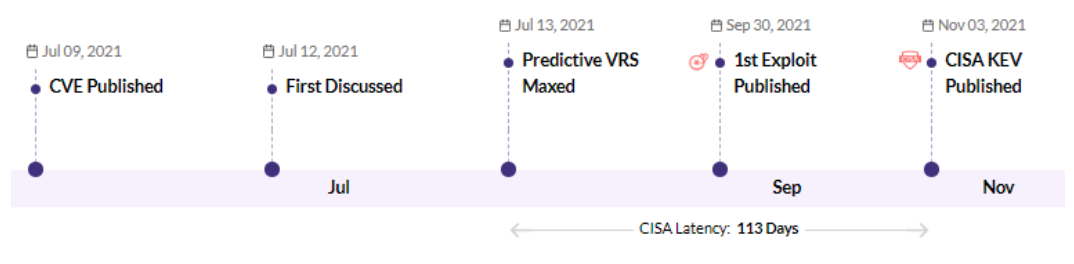
CVE-2021-27101 - Accellion FTA 9_12_370 and earlier SQL injection vulnerability - CISA KEV, Trending - 1 Ransomware / 1 APT
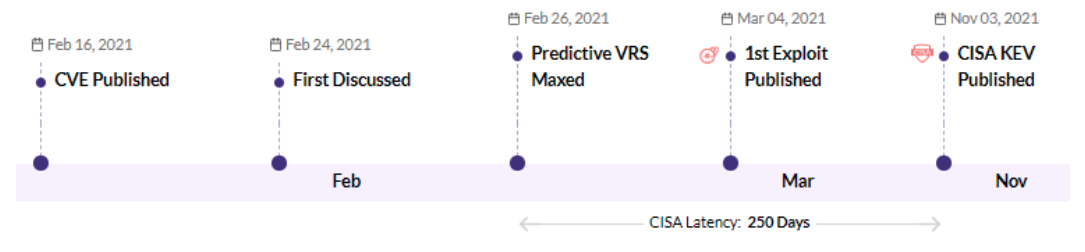
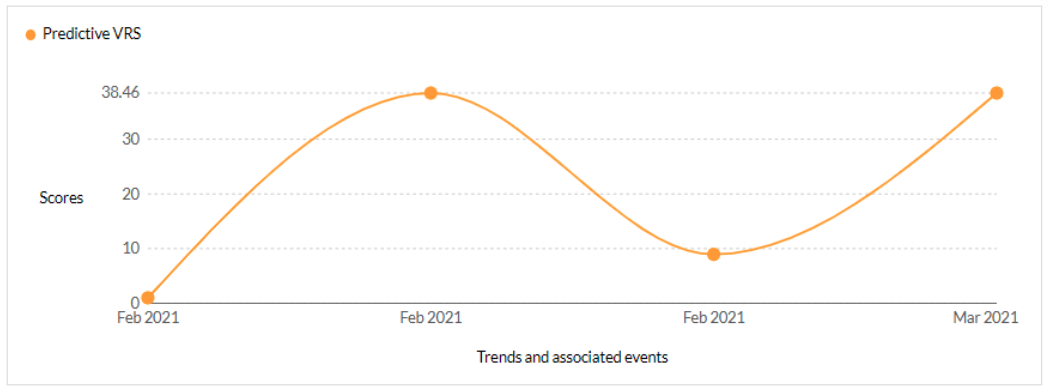
CVE-2021-27102 - Accellion FTA 9_12_411 and earlier OS Command execution vulnerability - CISA KEV, Trending - 1 Ransomware / 1 APT
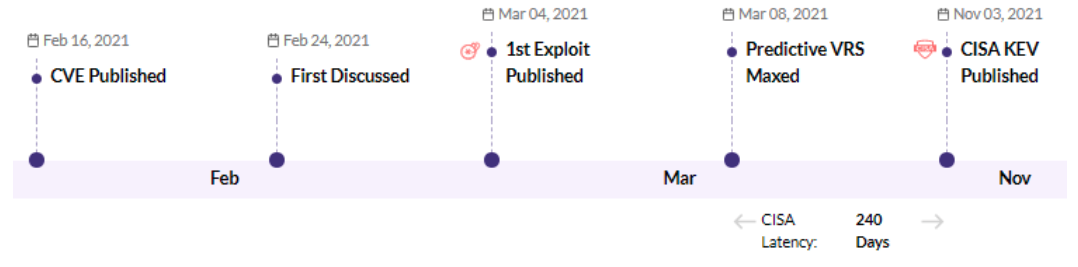
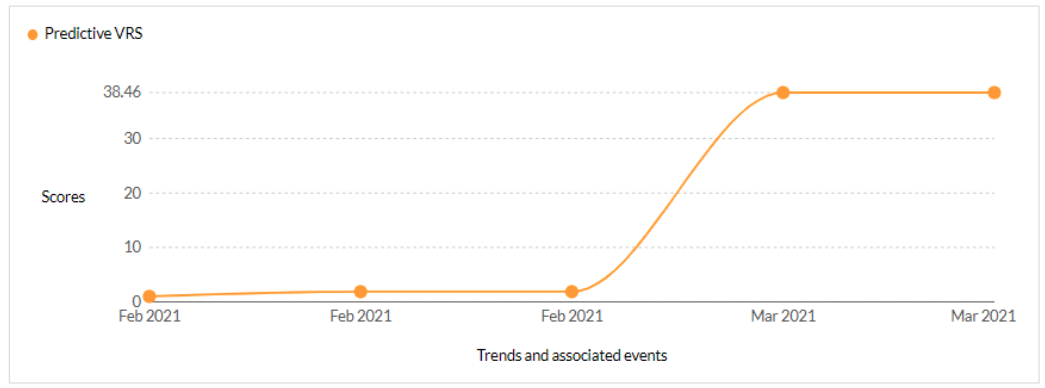
CVE-2021-27103 - Accellion FTA 9_12_411 and earlier SSRF vulnerability - CISA KEV - 1 Ransomware / 1 APT
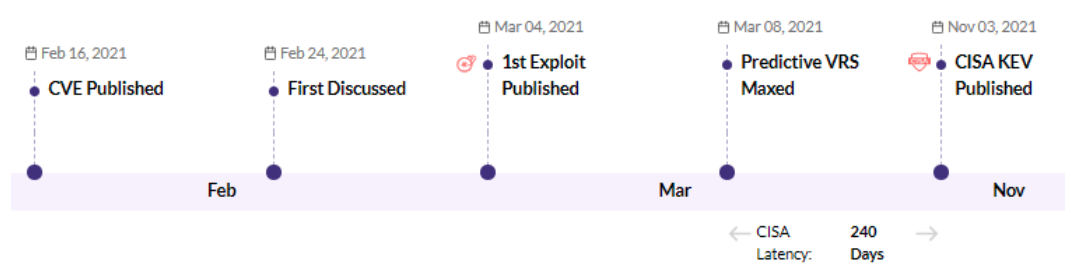
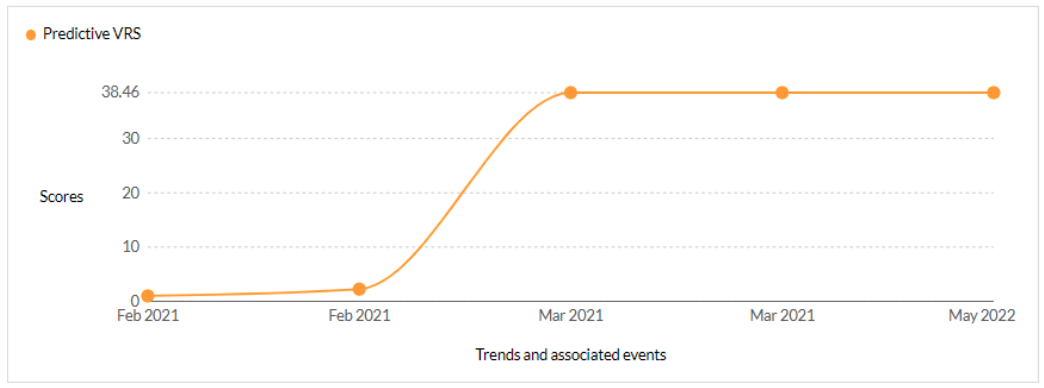
CVE-2021-27104 - Accellion FTA 9_12_370 and earlier OS Command Execution vulnerability - CISA KEV, Trending - 1 Ransomware / 1 APT
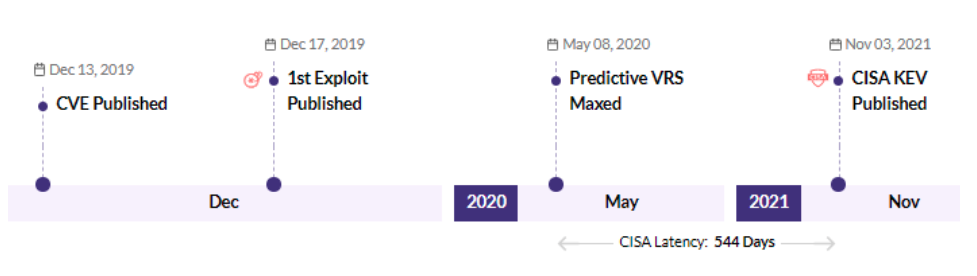
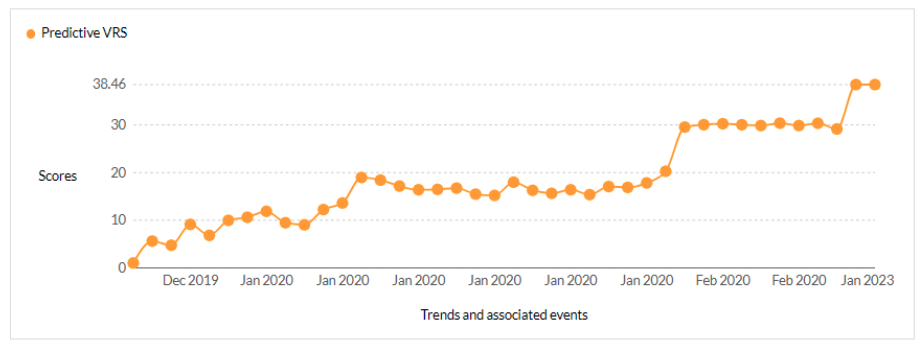
Securin experts were able to warn customers about the likelihood of attacks leveraging this vulnerability, 365 days ahead of scanners like Nessus and Nexpose.
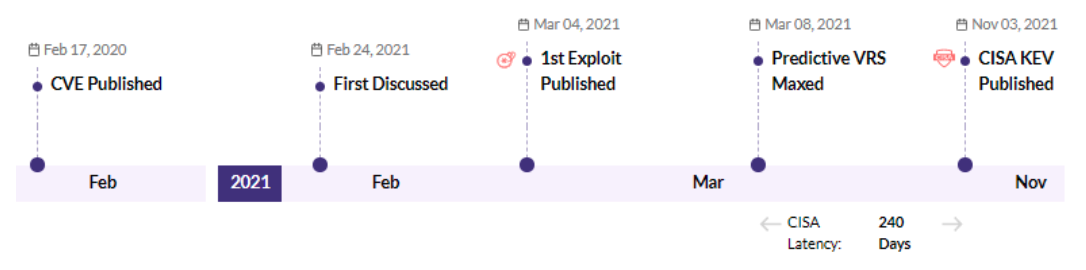
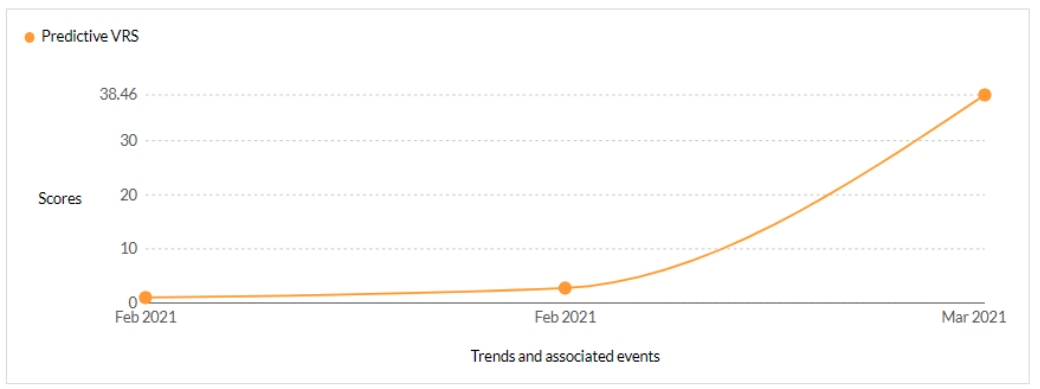
CVE-2023-0669 - Fortra GoAnywhere MFT pre-authentication command injection vulnerability - CISA KEV, Trending - 1 Ransomware / 1 APT
Securin experts were able to warn customers about the likelihood of attacks leveraging this vulnerability, six days ahead of Nessus and Qualys scanners.
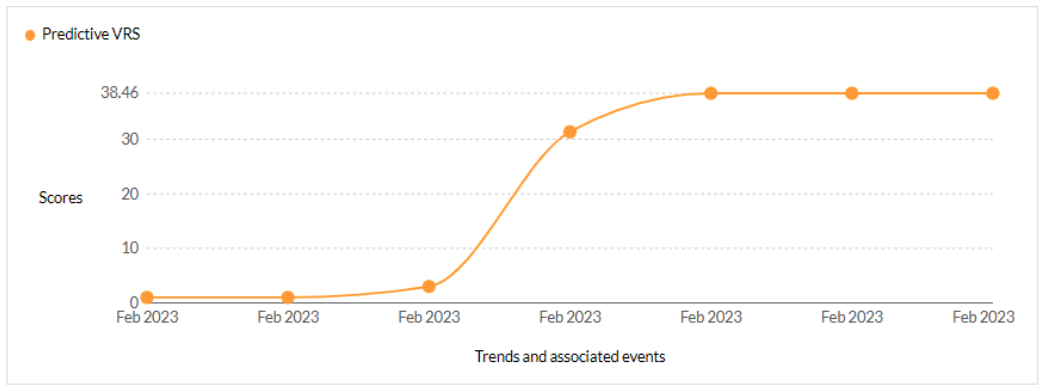
CVE-2023-27350 - This vulnerability allows remote attackers to bypass authentication on affected installations of PaperCut NG 22.0.5 (Build 63914). - CISA KEV, Trending - 3 Ransomware / 3 APT
Securin experts were able to warn customers about the likelihood of attacks leveraging this vulnerability, five days ahead of Qualys scanners.
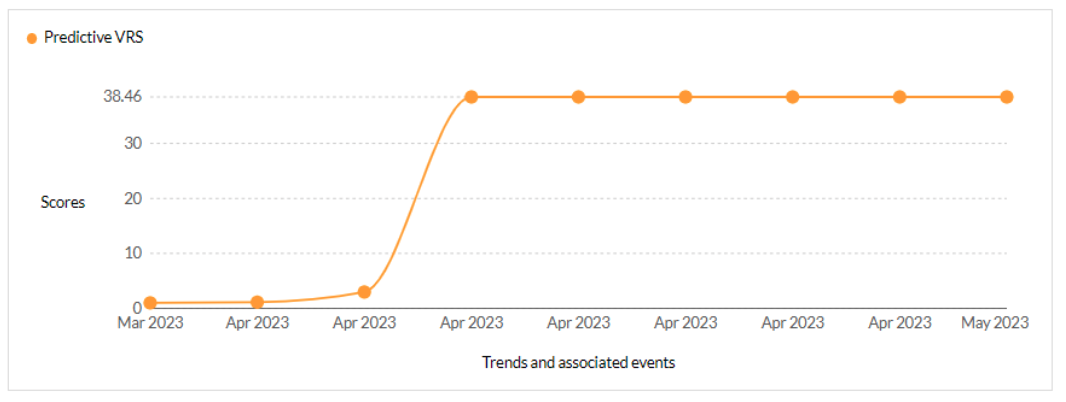
CVE-2023-27351 - This vulnerability allows remote attackers to bypass authentication on affected installations of PaperCut NG 22.0.5 (Build 63914). - Trending - 2 Ransomware / 1 APT
Securin experts were able to warn customers about the likelihood of attacks leveraging this vulnerability, five days ahead of Qualys scanners.
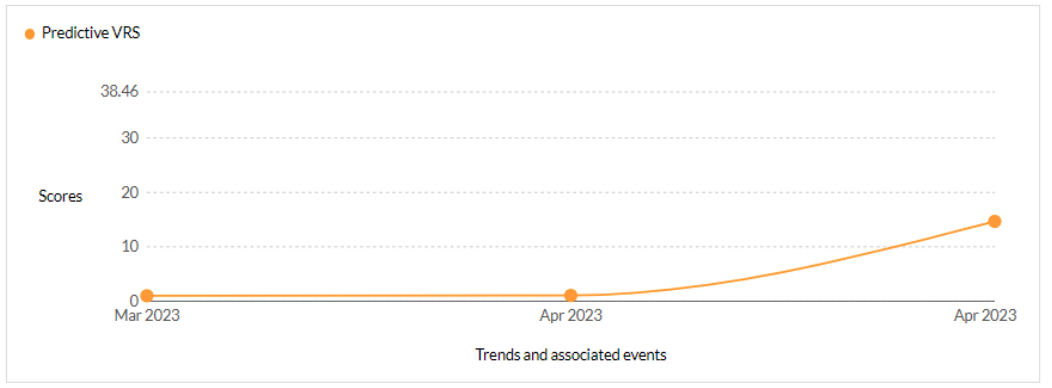
CVE-2023-34362 - This vulnerability allows unauthenticated remote attackers to gain access into Progress MOVEit Transfer server versions before 2021.0.6 (13.0.6), 2021.1.4 (13.1.4), 2022.0.4 (14.0.4), 2022.1.5 (14.1.5), and 2023.0.1 (15.0.1). - CISA KEV, Trending - 1 Ransomware / 2 APT
Cl0p’s announced in early June that they had been testing the now-patched MOVEit server vulnerabilities since 2021. Though still not ascertained if Cl0p is exploiting the following vulnerabilities, it is probable that they are.
CVE-2023-35036 - This vulnerability allows unauthenticated remote attackers to gain access into Progress MOVEit Transfer server versions before 2021.0.7 (13.0.7), 2021.1.5 (13.1.5), 2022.0.5 (14.0.5), 2022.1.6 (14.1.6), and 2023.0.2 (15.0.2). - Trending - 1 Ransomware*
CVE-2023-35708 - This vulnerability allows unauthenticated remote attackers to gain access into Progress MOVEit Transfer server versions before 2021.0.8 (13.0.8), 2021.1.6 (13.1.6), 2022.0.6 (14.0.6), 2022.1.7 (14.1.7), and 2023.0.3 (15.0.3). - Trending - 1 Ransomware*
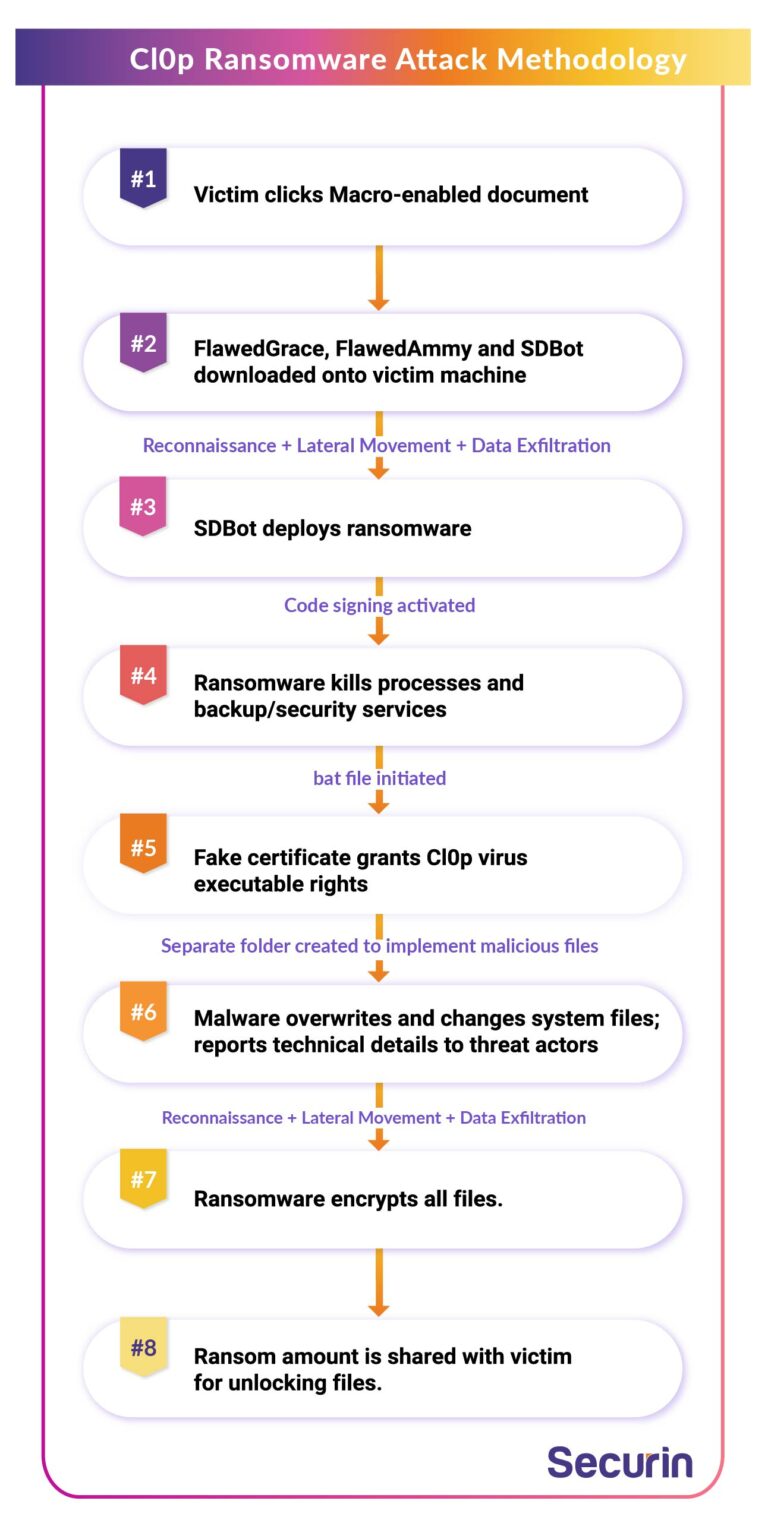
Cl0p Ransomware Attack Methodology
Cl0p ransomware was first spotted by Securin experts delivering a final payload for a phishing campaign run by TA505. The phishing emails would lead victims to a macro-enabled document that would drop a loader called Get2. The loader would then download various tools such as FlawedGrace, FlawedAmmy and SDBot, that were leveraged by the threat actor. Upon gaining a foothold on a victim’s machine, reconnaissance was conducted parallelly, alongside lateral movement and data exfiltration, to prepare for deployment of the ransomware. The SDBot payload has been observed delivering Cl0p ransomware.
Once Cl0p ransomware is deployed, it activates several features like code signing, to help it avoid detection. The ransomware usually tries to kill several processes and services relating to backups or security solutions, and does not deploy if it detects being run in a virtual environment.
Once the ransomware is injected into the system, a fake certificate is issued to grant executable rights to the Cl0p virus to elevate privileges and initiate a .bat file. The file then allows malware to overwrite and change system files. It also reads technical details such as computer names and shares them with the threat actors. The ransomware also creates a separate folder where more malicious files are implemented.
Cl0p ransomware then examines the victim computer for files to encrypt. Regularly used files such as .jpg, .mp3, .doc, etc are targeted in the encryption process. Once the encryption process is complete, all encrypted files get a .Clop extension to their titles and becomes impossible to access.
The victims then need to pay the ransom amount in order to remove Cl0p ransomware and facilitate in unlocking the files and recovering the data.
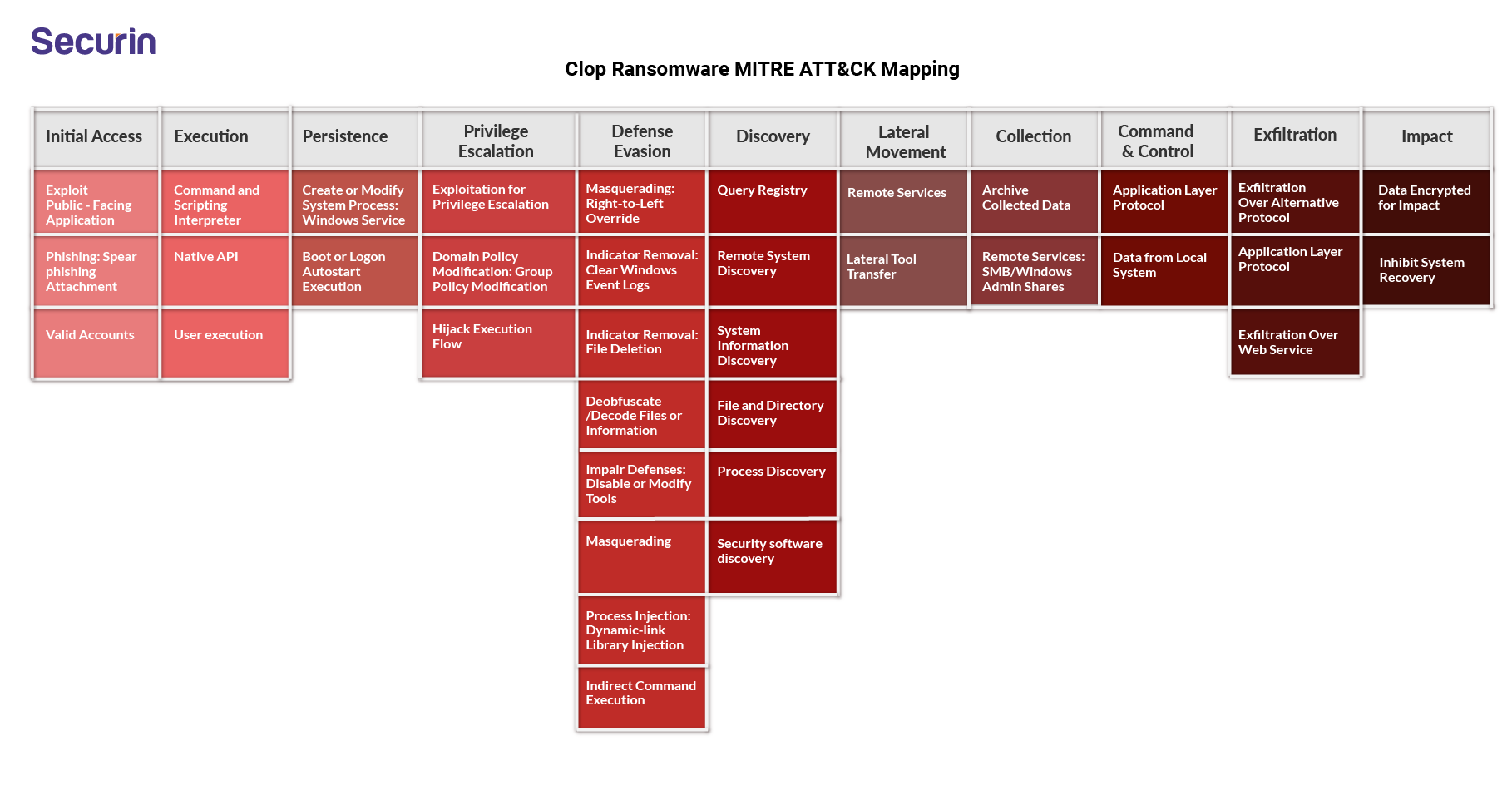
Cl0p Ransomware MITRE MAP with IOCs
Clop Ransomware IOCs | |
| Domains |
hxxp[:]//6v4q5w7di74grj2vtmikzgx2tnq5eagyg2cubpcnqrvvee2ijpmprzqd[.]onion hxxp[:]//santat7kpllt6iyvqbr7q4amdv6dzrh6paatvyrzl7ry3zm72zigf4ad[.]onion protected][.]com codeload[.]github[.]com hxxps://dsfdsfgb[.]azureedge[.]net/332_332/universupdatepluginx84.zipUnknown0c435aadaa3c42a71ad8ff80781def4c8ce085f960d75f15b6fee8df78b2ac38 hxxps://codeload[.]github[.]com/downloader2607/download64_12/zip/refs/heads/mainads[.]softupdt[.]com hxxps://cdn[.]discordapp[.]com/attachments/1004390520904220838/1008127492449648762/Setup_64_11.zipUnknown hxxps://spideroak[.]com/storage/OVPXG4DJMRSXE33BNNPWC5LUN5PTSMRTGAZTG/shared/5392194-1-1040/Setup_64_1.zip?b6755c86e52ceecf8d806bf814690691146[.]70[.]93[.]10f18a54ba72df1a17daf21b519ffeee8463cfc81c194a8759a698709f1c9a3e87 aviadronazhed[.]com guteyutur[.]com hxxp://27[.]70[.]196/km1 hxxp://91[.]38[.]135[.]67/km1 |
| Emails | unlock[@]support-mult.com |
| Emails | unlock[@]rsv-box.com |
| IP Address | 146[.]70[.]93[.]10 |
| SHA-1 Hash |
ba5c5b5cbd6abdf64131722240703fb585ee8b56 4fa2b95b7cde72ff81554cfbddc31bbf77530d4d ac71b646b0237b487c08478736b58f208a98eebf 77ea0fd635a37194efc1f3e0f5012a4704992b0e a1a628cca993f9455d22ca2c248ddca7e743683e 40b7b386c2c6944a6571c6dcfb23aaae026e8e82 46b02cc186b85e11c3d59790c3a0bfd2ae1f82a5 a6e940b1bd92864b742fbd5ed9b2ef763d788ea7 |
| SHA-256 Hash |
09d6dab9b70a74f61c41eaa485b37de9a40c86b6d2eae7413db11b4e6a8256ef d1224c08da923517d65c164932ef8d931633e5376f74bf0655b72d559cc32fd2 0b214297e87360b3b7f6d687bdd7802992bc0e89b170d53bf403e536e07e396e 0c435aadaa3c42a71ad8ff80781def4c8ce085f960d75f15b6fee8df78b2ac38 09247f88d47b69e8d50f0fe4c10c7f0ecc95c979a38c2f7dfee4aec3679b5807 a9d5ec72fad42a197cbadcb1edc6811e3a8dd8c674df473fd8fa952ba0a23c15 e8d98621b4cb45e027785d89770b25be0c323df553274238810872164187a45f 8e91f3294883fbdc31ff17c3075f252cbfdc1fc9145c6238468847f86d590418 d1c04608546caf39761a0e390d8f240faa4fc821eea279f688b15d0b2cfc9729 3320f11728458d01eef62e10e48897ec1c2277c1fe1aa2d471a16b4dccfc1207 eba8a0fe7b3724c4332fa126ef27daeca32e1dc9265c8bc5ae015b439744e989 cf0a24f1cdf5258c132102841d5b13e1c6978d9316ba4005076606dc60ec761b 389e03b1a1fd1c527d48df74d3c26a0483a5b105f36841193172f1ee80e62c1b 85c42e1504bdce63c59361fb9b721a15a80234e0272248f9ed7eb5f9ba7b3203 cb36503c08506fca731f0624fda1f7462b7f0f025a408596db1207d82174796a af1d155a0b36c14626b2bf9394c1b460d198c9dd96eb57fac06d38e36b805460 ad320839e01df160c5feb0e89131521719a65ab11c952f33e03d802ecee3f51f |
Interesting Trends
-
Cl0p Ransomware likes to MOVEit: Cl0p ransomware claimed responsibility of using the now-patched MOVEit zero-day vulnerability, and has led to 106 organizations worldwide being affected by the exploitation.
Read our MOVEit vulnerabilities article to learn more.
- Linux Malware Flaw: The Linux malware that was used in the 2022 attacks seems to have a flaw in the encryption scheme that has allowed the victims to recover their files for free for several months. The Cl0p Linux malware is considered an early prototype as it is plagued by several flaws and still does not have proper obfuscation and evasiveness mechanisms in place.
- Direct Emails to Victims: The Cl0p ransomware gang pioneered an innovation by pushing more victims into paying an extortion demand by simply emailing the victim’s customers and partners directly, warning of probable data leaks onto the dark web unless ransom demands were met.
- Novel Ransom Payment Schemes: Several new methods for infecting victims and convincing them to pay are constantly devised by ransomware groups. One method revolved around healthcare organizations offering consultations over the Internet, where booby-trapped medical records would be sent to the centers posing as ‘patients’. The second method involved carefully editing email inboxes of public company executives to make it appear that some kind of insider trading was involved. The methods were leveraged by the Cl0p group in accordance with a newer ransomware affiliate, Venus.
- Cyber Police Arrests in Ukraine: The Ukrainian police arrested 21 people who are likely members of or affiliates of the Cl0p ransomware gang. The hackers had targeted foreign businesses based in the United States and South Korea, used double extortion techniques, dropped the FlawedAmmyy RAT and used Cl0p encryption software to decipher stolen data.
- Disabling Windows Defender: Cl0p ransomware, formerly known as CryptoMix ransomware, devised a way to disable Windows Defender as well as remove the Microsoft Security Essentials anti-ransomware programs.
- FIN7 uses Cl0p Ransomware: APT Group FIN7 was observed dropping Cl0p Ransomware in attacks in April 2023, its first campaign since 2021. The FIN7 attackers utilized a PowerShell-based POWERTRASH in-memory malware dropper to deploy Lizar post-exploitation tool on compromised devices.
- Malware Variant Targeting Linux: The Cl0p ransomware gang first used the malware variant that specifically targets Linux servers during an attack against a university in Colombia in December 2022.
- Using TrueBot malware in attacks: Securin researchers noticed a spike in infected devices with TrueBot malware downloader, created by a Russian hacking group called Silence. While conducting the analysis our researchers found that Cl0p ransomware used TrueBot malware to access networks in an attack. TrueBot, typically is a first-stage module that collects information and takes screenshots, and helps in exfiltration of Active Directory trust relations information that enhances a threat actor’s post-infection activity. In the second phase, a C2 server instructs TrueBot to load shellcode or DLLs in memory, download EXEs, BATs, PS1 files, uninstall itself or execute other modules. In its post-compromise phase, TrueBot is used to drop Cobalt Strike beacons or FlawedGrace or GraceWire malware that is attributed to the TA505 threat group.
- Operation Cyclone: An international law enforcement operation led by Interpol, with a duration of 30 months, was launched targeting members of the Cl0p ransomware group, leading to the arrest of six key members of the gang and recovery of $185,000 worth of assets.
- Cl0p uses Raspberry Robin Worm in Attacks: In October 2022, Microsoft researchers observed Raspberry Robin infections after Cobalt Strike beacons were dropped by a threat actor tagged as DEV-0950. DEV-0950’s activity also involved a TrueBot infection that eventually deployed Cl0p ransomware.
Cl0p Ransomware - Prevention and Cure
The Cl0p ransomware group has become ever more prolific after the exploitation of the MOVEit Transfer and GoAnywhere MFT vulnerabilities and has been gaining preference as a favored payload for many threat actors. With this in mind, here are some measures that organizations can adopt to stay safe from a ransomware attack.
- Patch the vulnerabilities used by the group, and ensure no unused ports/instances are left hanging.
- Ensure that they tune into and follow weekly threat intelligence updates by cybersecurity providers to stay on track with latest developments.
- Set up multi-factor authentication, implement session timeouts, and practice good password hygiene.
- Perform a regular Attack Surface Management scan to discover exposures in your assets, domain controllers, active directories, servers, and all cloud-connected deployments.
- Perform a penetration test on your systems to identify if they are vulnerable via unidentified exposures.
- Regularly back up data in secure storage devices.
How We Can Help?
Securin has been researching ransomware groups and the methods they use to invade networks since 2019. Our comprehensive database of more than 359 vulnerabilities (and counting) used by ransomware groups is the most extensive compilation in the industry today. Securin’s expertise in ransomware research translates into our Ransomware reports and Ransomware Assessment service that can help organizations increase their security posture.