This edition brings you early warnings, trending news about cyber threats, and the accurate threat context. Check out which threat group is on the rampage, what vulnerability it could soon weaponize, and more.
Why play catch up when you can fix it now?
Trending Threats
- CISA Adds 3 New CVEs to the KEV Catalog
- Microsoft Fixes 80 Flaws on February Patch Tuesday
- New Malware from RedEyes: M2RAT
- Clop Ransomware Exploits GoAnywhere Zero-day to Breach 130 Organizations
- New Scar Rental Botnet – GooberBot
- New Chinese APT Group – Dalbit (m00nlight)
- Microsoft Exchange ProxyShell Vulnerabilities Exploited
Vulnerabilities to Watch Out For
Trending Threats
CISA has taken special notice of the vulnerability now because North Korean nation-state hackers are said to have weaponized this exploit.
CVE-2023-0669 is the GoAnywhere MFT zero-day vulnerability that hackers are actively exploiting now. Clop ransomware has breached more than 130 organizations by exploiting this vulnerability.
CVE-2015-2291 impacts Intel ethernet diagnostics driver for Windows (IQVW32.sys and IQVW64.sys). Exploiting this vulnerability can allow an attacker to drive the device into a denial-of-service state. Recently, the Scattered Spider APT group has been exploiting this vulnerability in the wild.
On 14 Feb 2023, CISA added 4 more CVEs to the KEV – CVE-2023-23376, CVE-2023-21715, CVE-2023-21823, and CVE-2023-23529. All these vulnerabilities were added to the KEV catalog after the vendor, Microsoft released patches for them on February Patch Tuesday.
CVE-2023-23376 is a privilege escalation flaw in Windows common log file system driver. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could gain SYSTEM privileges.
CVE-2023-21715 is a feature bypass vulnerability in Microsoft Publisher. An authenticated attacker could exploit the vulnerability by convincing a victim, through social engineering and attack the local device.
CVE-2023-21823 is a Windows graphics component remote code execution vulnerability that can grant SYSTEM privileges to an attacker.
CVE-2023-23529 is Apple’s type confusion issue that can be exploited for arbitrary code execution by getting the targeted user to access a malicious website. It is actively being exploited now.
On Feb 16, 2023, CVE-2022-46169 was also added to the Known Exploitable Vulnerabilities Catalog. This vulnerability is a critical command injection flaw found in the Cacti monitoring solution. It allows an unauthenticated user to execute arbitrary code on a server running Cacti, if a specific data source was selected for any monitored device. Since an exploit for it was published, attackers have been actively exploiting this vulnerability in Cacti. CVE-2022-46169 was patched in December 2023.
CISA Adds 3 New CVEs to the KEV Catalog
On 10, Feb 2023, CISA added CVE-2022-24990, CVE-2023-0669, and CVE-2015-2291 to the KEV catalog.
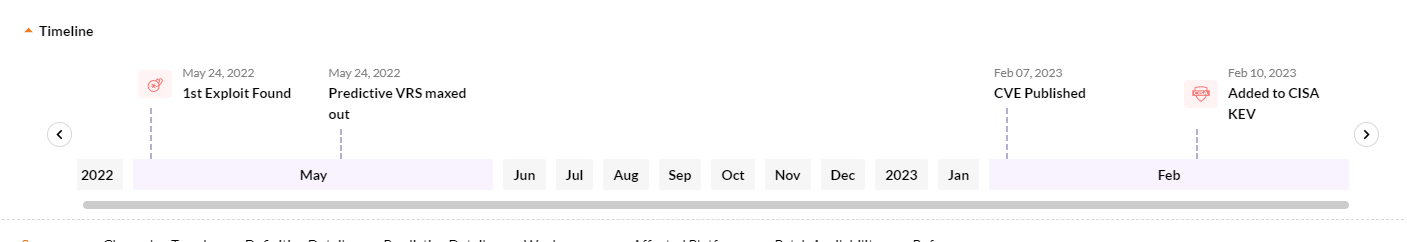
CVE-2022-24990 is the TerraMaster RCE vulnerability that affects their network-attached storage (TNAS) devices. An unauthenticated attack can also execute commands by exploiting this vulnerability. Given below is an image of the vulnerability’s progression since discovery.
Microsoft Fixes 80 Flaws on February Patch Tuesday
These include 3 actively exploited zero-days – CVE-2023-23376, CVE-2023-21715, and CVE-2023-21823. Other notable fixes include 12 elevation of privilege vulnerabilities, 2 security feature bypass vulnerabilities and 38 remote code execution vulnerabilities.
You can find all the updates here.
New Malware from RedEyes: M2RAT
RedEyes AKS ScarCruft has been using a new malware strain called M2RAT in their attacks on individuals for intelligence collection. This new malware uses a shared memory section for commands and data exfiltration and leaves very few operational traces on the infected machine. Initial access to victims’ devices involves phishing emails with malicious attachments. The attachments are sometimes JPG image files which use steganography for malicious activity. Using steganography, attackers can hide code inside image files, to stealthily introduce the M2RAT executable (“lskdjfei.exe”) onto the system and inject it into “explorer.exe.” This malware can perform keylogging, data theft, command execution, and then take screenshots from the desktop. It can also be used to exfiltrate data from phones. Before exfiltration, the stolen data is compressed in a password-protected RAR archive, and the local copy is wiped from memory to eliminate any traces.
Clop Ransomware Exploits GoAnywhere Zero-day to Breach 130 Organizations
Last week we learnt of the zero-day vulnerability in GoAnywhere MFT application, CVE-2023-0669. More than 1000 administrative ports of this solution are exposed to the public internet. It is now discovered that the Clop ransomware group has been exploiting this vulnerability to breach servers in around 130 organizations and steal their data. The group claimed that they could even move laterally through their victims’ networks and deploy ransomware payloads to encrypt their systems but resigned to just stealing the data for the time being. There is no news on ransom demands from the group or the affected organizations.
The MFT vulnerability has received two patches from Forta since its disclosure. One emergency patch was released immediately after the discovery and the other which can be accessible only after logging in with a user account. All GoAnywhere MFT users should apply these patches without delay.
New Scar Rental Botnet - GooberBot
The Scar rental botnet is a malware service that attackers can buy for low-cost attacks. Their latest development is the GooberBot which exploits CVE-2022-30525, CVE-2021-22205, and CVE-2021-35394. More than 10 products are affected by these vulnerabilities and exploits are also available for CVE-2022-30525 and CVE-2021-22205 . The malware is said to be still in development. There are 3 versions of the malware. In the first version, the botnet communicates with the C2 server in plaintext directly instead of encrypted data. In the next version, an encryption algorithm was used in communication. In the latest version, the single instance check method was changed to determine if the network communication of the C2 server is established.
New Chinese APT Group - Dalbit (m00nlight)
This new Chinese APT group calls itself Dalbit (moonlight in Korean) and targets Korean companies. This group relies on open-source tools to profile themselves and sometimes leaves some infected companies as proxies and download servers. They later use them as means to communicate with the threat actor upon infiltration of another company. Dalbit targets small-mid range companies in multiple sectors and exploits them for ransom. Dalbit targets three vulnerabilities:
CVE-2018-8639 and CVE-2019-1458: Elevation of privilege vulnerabilities that exist in Windows when the Win32k component fails to properly handle objects in memory.
CVE-2017-10271: Vulnerability in the Oracle WebLogic Server component of Oracle Fusion Middleware (subcomponent: WLS Security). Easily exploitable vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers with network access via T3 to compromise Oracle WebLogic Server. Successful attacks of this vulnerability can result in the takeover of the Oracle WebLogic Server.
Microsoft Exchange ProxyShell Vulnerabilities Exploited
Threat actors are targeting the proxyshell vulnerabilities CVE-2021-34473 and CVE-2021-34523 to deliver ProxyShellMiner to Windows endpoints in a highly evasive malware campaign. After initial access and successful delivery of the malware, the attackers compromised the mail servers that host the malware-dependent files. The malware requires a command line parameter to be supplied upon execution. This parameter is later used as a key for the XMRig miner configuration, and as an anti-runtime analysis tactic. The malware uses XMrig (Open source cryptocurrency miner) to mine cryptocurrency in the compromised systems.
Exchange servers that contain the remote code execution vulnerability CVE-2021-34473 and the privilege escalation vulnerability CVE-2021-34523 are targeted in these attacks. Organizations using Microsoft Exchange servers should take steps to immediately patch these vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities to Watch Out For
Zero-day Vulnerability in Apple’s iPhones, Macs
CVE-2023-23529 is a WebKit confusion flaw that can allow arbitrary code execution and trigger OS crashes on compromised devices. An attacker can achieve this by sending maliciously crafted web content. Apple addressed this vulnerability with improved checks in iOS 16.3.1, iPadOS 16.3.1, and macOS Ventura 13.2.1.
CVE-2023-25194: Remote Code Execution Flaw in Apache Kafka
CVE-2023-25194 was discovered in Apache Kafka Connect, a free, open-source component of Apache Kafka that operates as a central hub for data integration between systems, databases, and key-value stores. When exploited, it can lead to remote code execution or denial-of-service. However, it can only be triggered when there is access to a Kafka Connect worker – a logical work unit component – and the user must also be able to create or modify worker connectors with an arbitrary Kafka client SASL JAAS config and a SASL-based security protocol.
Apache released a patch for it and recommends that users update to the latest version.
CVE-2022-47986: IBM Aspera Faspex Vulnerability
This is a YAML deserialization flaw that can be exploited by a remote attacker for arbitrary code execution using specially crafted API calls. It was discovered in October 2022 and fixed in Jan 2023. It is classified as a high-severity vulnerability and more than 100 internet-exposed Aspera Faspex servers are available all over the world. An exploit concept for this vulnerability was recently published making it even more dangerous to leave it unpatched.
CVE-2023-20032: Critical Flaw in ClamAV Open-Source Antivirus Software
The CVE-2023-20032 vulnerability is found in the HFS+ file parser component of the antivirus software ClamAV. It has a critical rating of 9.8 on the CVSS scale and affects versions 1.0.0 and earlier, 0.105.1 and earlier, and 0.103.7 and earlier. If exploited, it could allow an attacker to run arbitrary code with the same privileges as that of the ClamAV scanning process, or crash the process, resulting in a denial-of-service (DoS) condition. CISCO has published an advisory for this vulnerability.
Follow our weekly Threat Intelligence Series and podcast for proactive alerts on trending threats.
